
The Sustainable Benefits of Growing Hydroponic Vegetables
In an era where environmental consciousness is paramount, the agricultural industry is continually seeking innovative and sustainable solutions to meet the growing demand for food. Hydroponic farming, a method of growing plants without soil, has emerged as a promising alternative with numerous sustainable benefits. This article explores the environmental advantages of cultivating vegetables through hydroponics, highlighting its potential to revolutionize modern agriculture.
Water Efficiency:
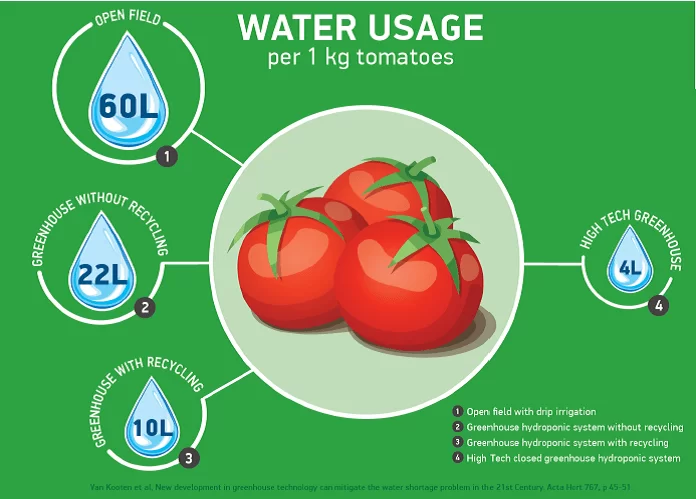
One of the significant sustainable benefits of hydroponic vegetable cultivation is water efficiency. Traditional soil-based farming often requires vast amounts of water, leading to water wastage through runoff and evaporation. Hydroponics, on the other hand, employs a closed-loop system, where water is recirculated within the system, significantly reducing water consumption. Studies have shown that hydroponic systems can use up to 90% less water compared to traditional farming methods, making it an eco-friendly choice in regions facing water scarcity.
Reduced Land Footprint:
Hydroponic farming allows for vertical and controlled growth, enabling the cultivation of vegetables in smaller spaces compared to conventional agriculture. This vertical farming approach minimizes the need for expansive land areas, making it possible to grow crops in urban environments or areas with limited arable land. The reduced land footprint helps conserve natural habitats, prevents deforestation, and allows for more sustainable land use.
Elimination of Chemical Runoff:
Traditional farming practices often involve the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, which can lead to harmful runoff, contaminating water sources and adversely impacting ecosystems. Hydroponic systems provide a controlled environment where nutrient solutions are directly delivered to the plants, eliminating the risk of chemical runoff. This not only safeguards water quality but also promotes healthier and more nutrient-dense vegetables for consumers.
Energy Efficiency:

Hydroponic systems can be designed with energy-efficient technologies, such as LED lighting and climate control systems. By optimizing light and temperature conditions, hydroponic farms can achieve year-round production and maximize crop yields. While energy consumption is a consideration, the overall efficiency of hydroponic systems often outweighs the energy inputs, especially when compared to the resource-intensive nature of traditional agriculture.
Increased Profitability:
Hydroponic farming's controlled environment and faster growth cycles contribute to increased productivity and, consequently, profitability. With reduced crop cycles and the ability to grow high-value crops, hydroponic farmers can often command premium prices in the market. Additionally, the ability to grow crops closer to urban centers reduces transportation costs, further contributing to the financial sustainability of hydroponic operations.
Reduced Labor Costs:
Hydroponic systems often involve less manual labor than traditional farming practices. Automated nutrient delivery systems, controlled environments, and optimized conditions reduce the need for constant monitoring and manual intervention. This not only decreases labor costs but also allows for more efficient and streamlined operations.
The bottom line:
The sustainable and financial benefits of growing hydroponic vegetables position it as a transformative solution for modern agriculture. From water and land efficiency to the elimination of chemical runoff and increased profitability, hydroponics offers a holistic approach that aligns with both environmental and financial sustainability goals. As the world seeks innovative and economically viable agricultural practices, hydroponics stands out as a promising investment that not only ensures food security but also enhances the financial viability of farming operations.