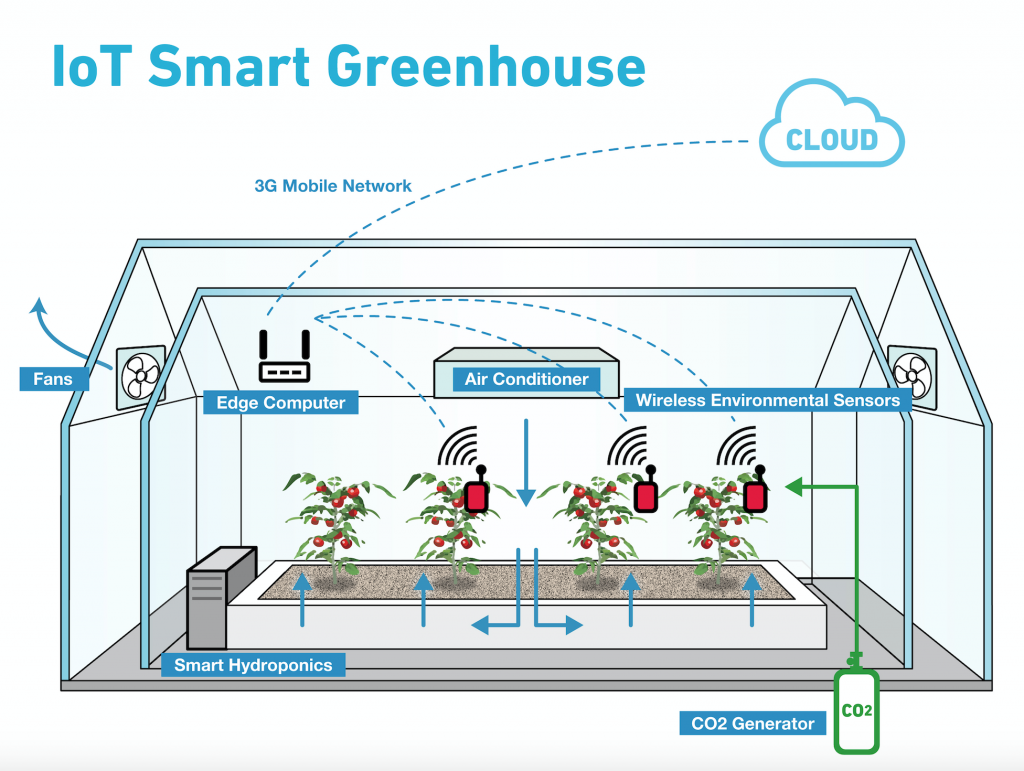
How IoT In Agriculture Works
There is the involvement of various smart sensors, devices, and data analytics platforms to collect, transmit, and analyze data from agricultural operations. Here’s a step-by-step process of IoT working in agriculture:
Sensing and Data Collection
Different environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, soil moisture, light intensity, and weather conditions are collected with different IoT devices and sensors deployed to the farm. The IoT sensors can be placed in plants, animals, soil, weather stations, etc.

Data Transmission
The transmitted data can be collected through various communication protocols such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi, satellite connections, etc. The selection of sensors depends on the range of devices, the size of farms, and the availability of network infrastructure.
Data Storage and Cloud Platforms
The collected data can be stored on local servers or cloud-based platforms. However, there is a great level of data scalability and accessibility when opting for cloud storage instead of local servers for handling vast amounts of data generated by multiple farms.
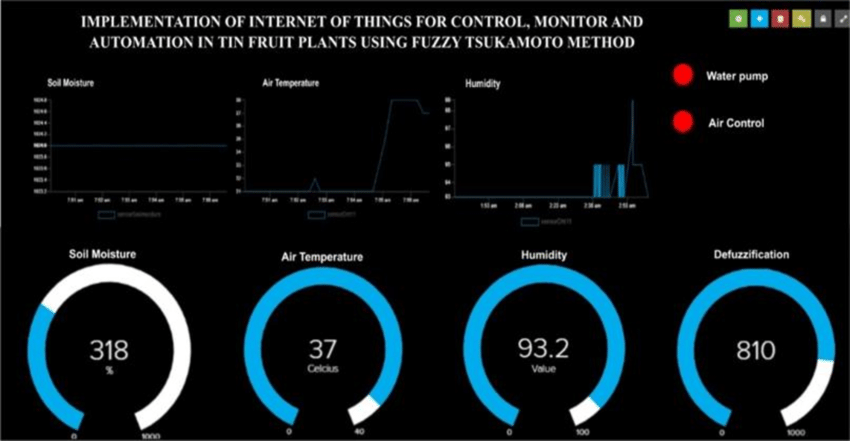
Data Analytics
There is a utilization of sophisticated data analytics algorithms and tools for analyzing and processing information. The analytics can reveal data patterns and trends that can be used for optimizing agricultural processes and making informed decisions.
Decision Making and Automation
Data collected for different purposes, such as scheduling, irrigation activities, pest control, and other farming activities, can be automated for carrying out specific actions, such as activating machinery or adjusting irrigation systems.
Blockchain for Traceability:
Blockchain technology is being explored for enhancing traceability in hydroponic farming. By recording every stage of the supply chain – from planting and harvesting to packaging and distribution – blockchain ensures transparency and traceability. Consumers can access detailed information about the origin and journey of the produce, promoting trust and accountability in the industry.
Remote Monitoring and Control
Using real-time monitoring tools allows farmers to optimize resource usage even if they are not physically present on the farm and can better manage the operations of their farm remotely through mobile applications or web interfaces.
Integration with Farm Management Software
The farmers can perform seamless data sharing and streamline the decision-making process by integrating IoT devices and platforms with existing farm management software or agriculture-specific applications.
Data Security and Privacy
Major data security practices such as data authentication, encryption, and restricted control access are implemented to protect sensitive information collected by IoT sensors.
Success stories when using technology applied to hydroponics
Bowery Farming, based in New Jersey, is a hydroponic vertical farm that leverages automation, machine learning, and data analytics to optimize every aspect of the growing process. Their proprietary BoweryOS platform monitors and adjusts variables such as light, nutrient levels, and temperature in real-time. By embracing technology, Bowery Farming achieves efficient resource utilization, reduces waste, and delivers fresh, locally grown produce to urban markets. This success story demonstrates the scalability and sustainability of technology-driven hydroponic farming
– Bowery Farming